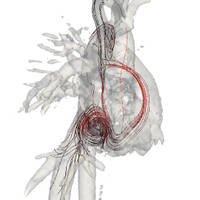
Analysis of 3D MRI Blood-Flow Data using Helmholtz Decomposition
Facts
| Type | master project |
|---|---|
| Place | BMT |
| Supervisors | Andrei Jalba, Roy van Pelt, Remco Duits |
| Student | Andrés Mauricio Arias |
| Thesis | will be available here |
| Start/End date | / 11-11-2011 |
Description
We present a method for obtaining a simplified representation of the blood-flow-field, acquired by Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The blood-flow provides an indication of the condition of the blood vessels and the cardiac muscle. However, the images acquired by MRI provide large and noisy data sets, which are hard to interpret. To facilitate the analysis of the unsteady blood-flow data, we aim for simplified and abstract representation of the velocity fields. In particular, we use the Helmholtz decomposition, which separates the flow field into a rotation-free, a divergence-free and an additional harmonic field. This decomposition can give us good insights of the behavior of the blood-flow, potentially better than other simplification methods. Several approaches are investigated to obtain the Helmholtz decomposition of the flow. Specifically, we use a multi-scale kernel method and a numeric method based on finite differences. We give a detailed description of the theory underlying these methods. The proposed methods are tested on artificial, simulated, and clinical datasets. The results showed that both methods were successfully implemented, where the decomposition clearly describes the vorticity and divergence of the flow. Also, the results of the decomposition might be valuable for research, aiming to find correlations between this representation of the blood-flow and cardiovascular diseases.